The voltage ratio in transformer´s windings depends on the number of turns of each winding and is calculated by the following formula:
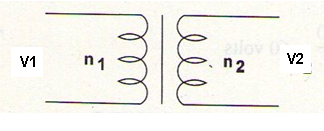
Formula 1
V1 / V2 = n1 / n2
Where:
V1 is the voltage applied to the primary winding in volts (V)
V2 is the voltage in the secondary winding in volts (V)
n1 is the number of turns in the primary winding
n2 is the number of turns in the secondary winding
Application Example:
A transformer has a primary winding formed by 1000 turns and a secondary winding formed by 500 turns. Calculate the secundary´s voltage when applying 12 V to the primary.
Data:
V1 = 12 V
V2 = ?
n1 = 1 000
n2 = 500
Applying formula 1:
12/V2 = 1000/500
1000 x V2 = 500 x 120
V2 = (120 x 500)/1000
V2 = 6 V




