The audio signal can be sourced to the circuit by the earphone jack or the loudspeaker connections. The sensitivity control allows the reader to find the correct operation point. The frequency response is determined by a capacitor in the range between 10 nF and 220 ?F.
Larger values give a low frequency response and lower values give a high frequency response. The device can be assembled like a module and installed in the car. Figure 1 shows the schematic diagram for the device.
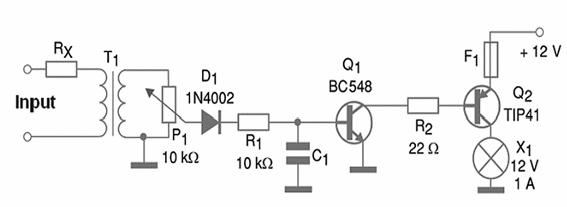
Figure 2 shows how the components are soldered to a terminal strip. The more experienced readers can assemble the circuit using a printed circuit board.
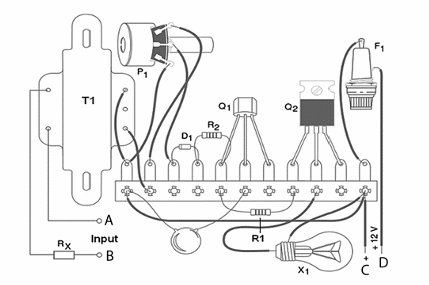
The heatsink for Q1 is a small metal plate bended to form a ‘U’. For the input signals, common wires can be used. The transformer is any type found in power supplies with a primary wound rated to 110 to 220 V and a secondary for 6 to 12 V and currents in the range between 100 and 500 mA.
Rx has a value determined by the output power of the amplifier. If the audio source is less than 1 W, you don’t need to use this resistor. The next table allows the selection of R1 according to the output power of the amplifier:
| Output Power (W) | Rx (?) |
| 0—1 | 0 |
| 1 to 5 | 47 |
| 5 to 20 | 100 |
| 20 to 50 | 220 |
| 50 and more | 470 |
Other resistors are 1/8 W or more and C1 can be a ceramic or polyester type. The Potentiometer is common and the device does not need an on/off switch. The power drain is zero when the input signal is off. D1 can be replaced by equivalents, like the 1N4004, 1N4148, etc.
To test, connect the A and B inputs to the wires from the loudspeaker of the sound equipment or the earphone output of any portable sound equipment. Connect points C and D to the power supply. Adjust the sound equipment to the desired volume and adjust P1 to a light effect as described. If you have problems to control the lamp, change Rx. If all is OK, you can use them, adjusting P1 every time you want the effects.
Semiconductors:
Q1 - BC548 or equivalent—general purpose silicon NPN transistor
Q2—TIP41—Power silicon NPN transistor
D1—1N4002 or equivalent—silicon diode
Resistors: (1/8W, 5%)
Rx—47 ? x 1 W—yellow, violet, black
R1— 10 k?—brown, black, orange
R2—22 ?—red, red, black
P1—10 k?—Potentiometer (lin or log)
Capacitor:
C1—see previous text
Other:
T1—transformer—see previous text
X1— 12 V, up to 1 A—incandescent lamp
F1—5 A—fuse
Terminal strip, plastic box, heatsink for Q2, fuse holder, knob for the Potentiometer, wires, solder, etc.




