This site explores many applications for solenoids such as the canon, the galvanometer, the magic pendulum, and projects performed with the laser Lissajous. Here is another application for solenoids: a simple project that launches a coin into the air in a completely random manner Without tricks or manipulations by the operator.
Objectives
Build a project that uses a solenoid as its basis.
Learn more about solenoids.
Use a coin tosser to get simple yes/no decisions.
How it Works
The basic idea is very simple: When energized, the magnetic field produced by a solenoid pulls a metallic core through the center of the coil. This fast movement launches a small coin into the air, as shown in Figure 1.
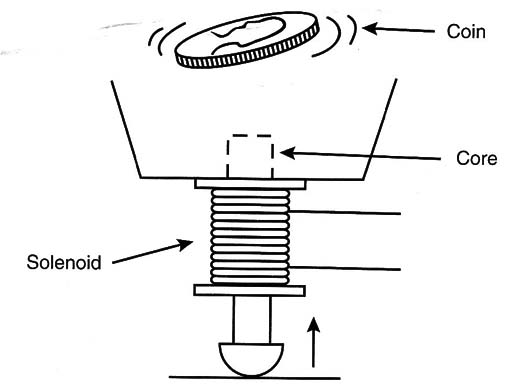
The critical issue is to build the solenoid strong enough to launch a coin when powered from C or D cells. Because enameled Wires come in many gauges and the magnetic field depends on the number of turns and current across the coil, a large range of construction possibilities must be examined by the reader.
In the text we will give the basic version, which has been tested by the author and provided good results.
But depending on the material used, mainly the weight of the core and dimensions of the solenoid, it will be necessary to test your project.
How to Build
Figure 2 shows the basic version of the simple coin tosser. The circuit can be powered by four C or D cells because the current required is too high to be sourced from AA cells (depending on the resistance of the wire used in the coil).
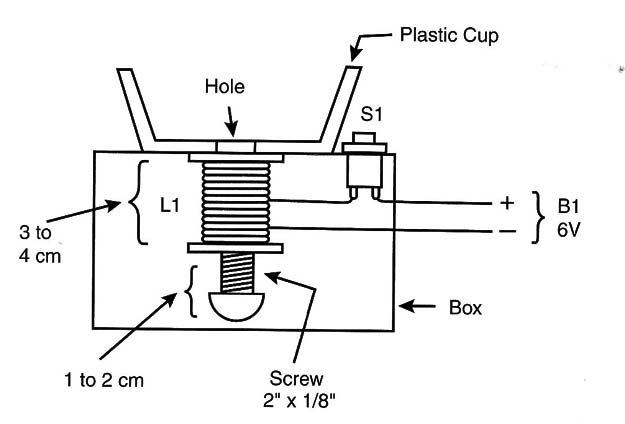
The coil is wound around a cardboard or plastic bobbin with the dimensions shown in the figure. The enameled copper wire can be 28- to 30-gauge wire, and the number of turns should be in the range of 200 to 500, according to the dimensions of the bobbin and the gauge of the wire. The core is a 2- >< 1/8-inch screw that must have free movement when sliding inside the coil.
Notice that the core must be partially inside the bobbin when the circuit is off.
You will need to experiment with the position so that when the coil is energized the core will be pulled inside.
Testing and Using
Adjust the position of the core inside the coil, as recommended previously.
Press S1 and verify if the core is pulled quickly toward the inside of the coil. If not, change the position of the core and/or change the number of turns of the coil. If the operation is okay, put a small coin in the tray and see if it is launched when S1 is pressed.
Parts List
L1 - Coil (see text)
S1 - Pushbutton (normally open (NO)
B1 - 6 volts of power (four C or D cells)
Wires, cell holder, core for the coil, solder, etc.
Cross Themes
A coin tosser can be used in experiments involving the random generation of probable situations. In science, a coin tosser that canlt be manipulated or tricked by the operator is very useful. Other applications with cross themes in the sciences are suggested here:
Use the project to generate random numbers
In statistics research.




