Utilities:
• Activation of utilities and automatisms through the touch of the fingers.
• Drive loads with resistive sensors such as water level detectors, which can replace X1.
• Drive by contact with conductive objects in automation or alarm systems.
Constructive Details:
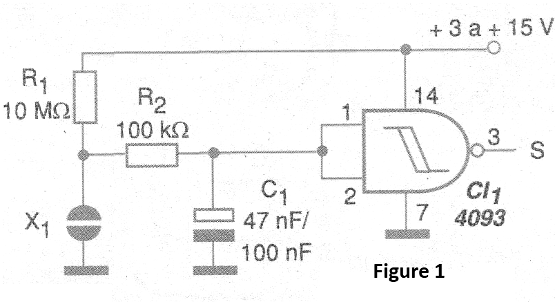
The circuit uses only one of the four trigger NAND ports available on the 4093 integrated circuit. Other ports can be used on similar keys or for other purposes.
The printed circuit board for one of the ports is shown in figure 2.
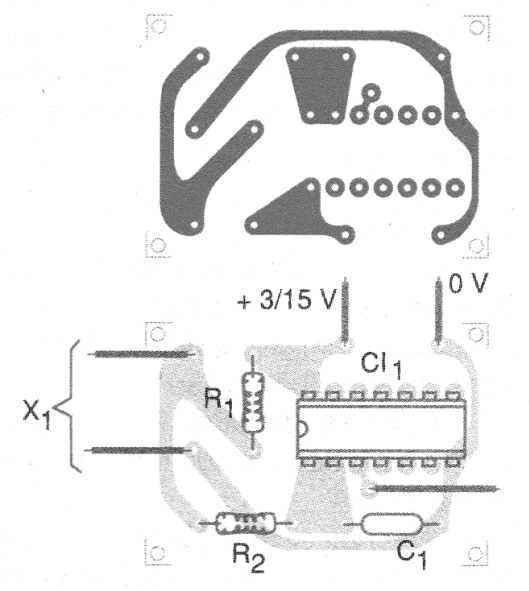
The sensor can be formed by two adjacent metal plates, which must be touched at the same time. R1 determines the sensitivity to the touch. With very large values care must be taken that dirt or moisture does not cause random drive of the circuit.
Recommended values are in the range of 100 k ohms to 22 M ohm. The power supply for this circuit must be isolated from the mains. Capacitor C1 determines the response of the circuit to noise and its value must be obtained experimentally mainly as a function of the length of the cable to the sensor.
If this cable is larger than 40 cm shielded wire must be used.
Semiconductor:
CI-1 - 4093 - CMOS integrated circuit
Resistors: (1/8 W, 5%)
R1 - 10 M ohm
R2 - 100 k ohm
Capacitor:
C1 - 47 nF to 100 nF - see text - ceramic or polyester
Several:
X1 - Sensor - see text
Printed circuit board, wires, solder, etc.