We can define "pneutronics" the science derived of the application at the same time of electronics and pneumatics.
Pressure
Is the amount of force per unit of area.
Formula
P = F/S
Where:
P is the pressure
F is the force
S is the area
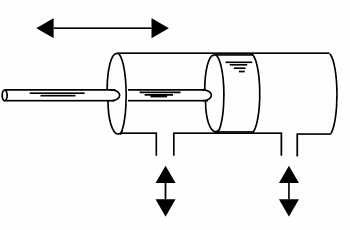
Air Pistons
Pistons can be used to change forces or displacements as shown by figure 1.
Tubes with pistons can also be used to transmit forces from one place to another as shown by the same figure.
Formulas
a) Forces:
F1/F2 = S1/S2
Where:
F1 - force applied to piston 1
F2 - resultant force in piston 2
S1 - area of piston 1
S2 - area of piston 2
b) Displacements:
d1/d2 = F1/F2
Where:
d1 - displacement of piston 1
d2 - displacement of piston 2
S1 - area of piston 1
S2 - area of piston 2
Gas Equation
Ideal gases obey this equation where the state of rarefied gas in a container is described.
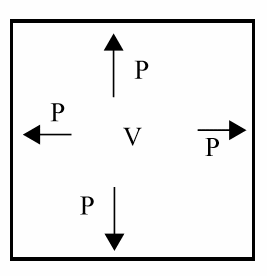
Formula
PV = nRT
Where:
P is the pressure of the gas
V is the volume of the gas
n is the mumber of moles (mass/molecular mass)
R is the gas constant = 0.0821 atm.l/moles.deg
Air Muscles
Air muscles are devices that can convert air pressure into mechanical force as shown by figure 3.
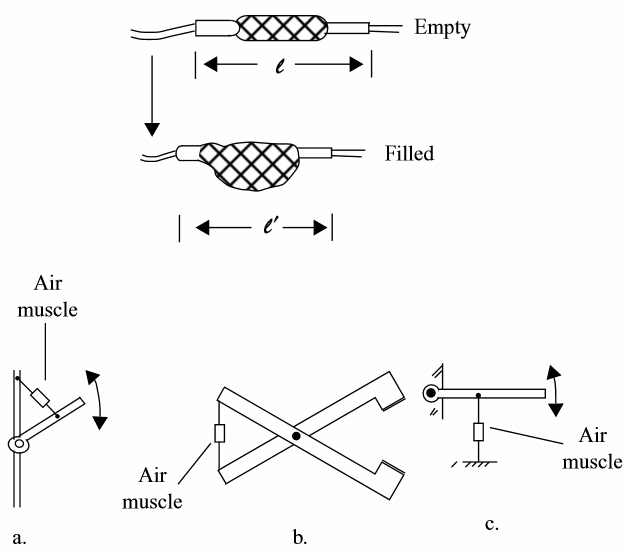
In the figure some applications for air muscles are shown.
(a) Arm
(b) Gripper
(c) Actuator



