Figure 1 shows a simple constant-current source. It uses an adjustable voltage regulator IC such as the LM150/LM317/LM350T or any equivalent. The LM350T, for instance, can provide a load with currents up to 3 A.
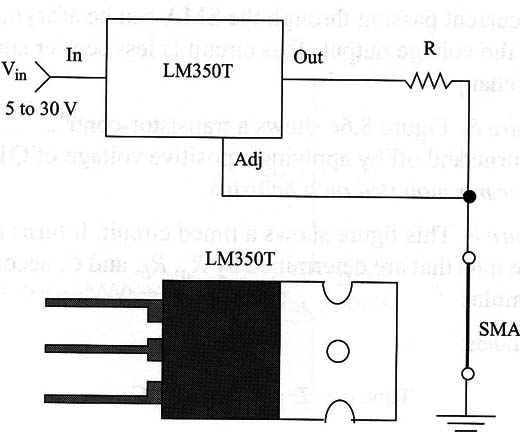
The value of R depends on the desired current in the load. It can be calculated using the next formula:
Formula:
R = 1.25/I
where
R = circuit resistance in Ω
I = required current to drive the SMA in amperes
In th formula, the 1.25 value is the internal reference voltage of ICs such as the LM150, LM350, and LM317. If another type of IC is used, the specification sheet will give the internal voltage reference to be substituted for the 1.25 value.
The value of Vin is derived from the resistance of the SMA or the voltage necessary to drive it. If we know the SMA resistance and the current passing through it, we can calculate the voltage required to drive it using Ohm’s law.
Formula:
V = Rsma x I
Where:
V = voltage across the SMA in volts
Rsma = resistance of the SMA in Ω
I = current in amperes
Vin must be at least 2 or 3 V higher than Vsma.



