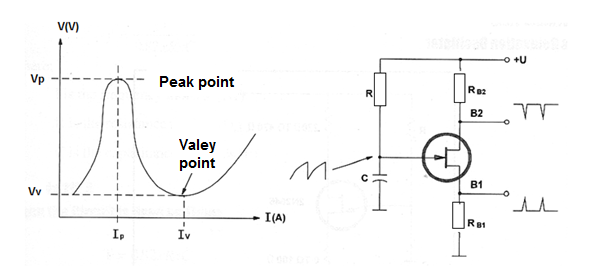
The Unijunction transistor (UJT) and also the programmable UJT are devices intend to be used in relaxation oscillators and timers. Figure 98 shows the equivalent circuit and the basic configuration to a relaxation oscillator using the UJT.
Formula 1
UJT peak voltage:
Vp = Vv + n x Vbb
Where:
Vp is the peak voltage in volts (V)
Vv is the foward biased voltage fall in the UJT internal diode (0.7 V)
n is the intrinsic standoff ratio (0.3 to 0.8 to typical UJT transistors)
VBB is the voltage between bases in volts (V)
Formula 2
Resistance between bases:
Rbb = Rb1 + Rb2
Where:
RBB is the resistance between bases in ohm (Ω)
RB1 and RB2 are the internal equivalent resistances in ohm (Ω)
Formula 3
As relaxation oscillator
Frequency:

Where:
f is the frequency in hertz (Hz)
R is the resistance in ohm (Ω)
C is the capacitance in farads (F)
n is the intrinsic standoff ratio
Derivated formula:
Formula 4
A simplyfied formula to calculate the frequency in a relaxation oscillator can be used in applications where precision is not required.
f = 1 / ( 0.82 x R x C )
Where
f is the frequency in hertz (Hz)
R is the resistance in ohm (Ω)
C is the capacitance in farads (F)
Formula 5
When the circuit is used as timer.
T = 0.82 x R x C
Where:
T is the period in seconds (s)
R is the resistance in ohm (Ω)
C is the capacitance in farads (F)
Application example:
Determine the resistance to be used in a relaxation oscillator using a UJT to make it run at 1 kHz with a 100 nF capacitor.
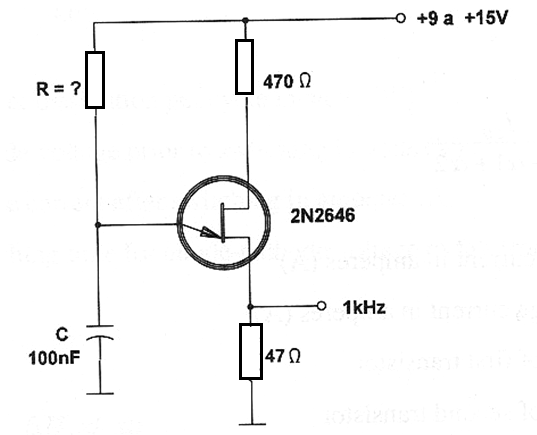
Data:
f = 1 000 Hz 103
C = 100 nF = 0.1 x 10-6 F
R = ?
Using formula 112.4:
103 = 1 / ( 0.82 x 0.1 x 10-6 x R )
Isolating R:
R = 1 / (0.82 x 0.1 x 10-6 x 103)
R = 1 / 0.082 x 10-3
R = 12.19 x 103
R = 12.19 kΩ



