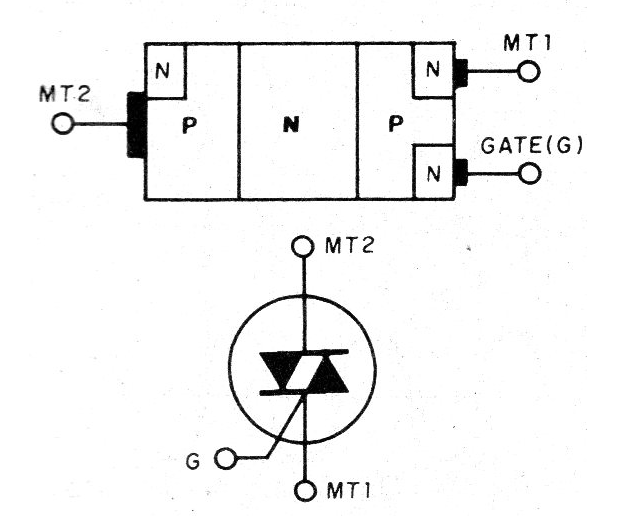
The Triac is a semiconductor switching device that can be considered as two SCRs connected in a manner that allows them to pass alternating current as shown in figure. So this device can be considered as two SCRs when making calculations.
Formula 1
Power dissipation:
Pd = Us x Id
Where:
Pd is the power dissipation in watts (W)
Us is the saturation voltage in volts (V)
Id is the forward current in amperes (A)
Note: to common Triacs the saturation voltage is around 1.5 volts.
Formula 2
Formula 5 used to SCRs when applied in full wave circuits are valid to calculation involving the load voltage as function of the conduction angle.
UL = (Up / π) x (1 + cos α)
Where:
UL is the instantaneous value of the load voltage in volts (V)
Up is the peak value of the sine input voltage in volts (V)
π is 3.1416
cos α is the cosine of the conduction angle in (angle in degrees)
Application Example:
Calculate the power dissipated by a triac when used in a circuit controlling a 10 A load. The saturation voltage is 1.5 V.
Data:
Us = 1.5 V
Id = 10 A
Pd = ?
Using formula 1:
Pd = 10 x 1.5 = 15 watts



