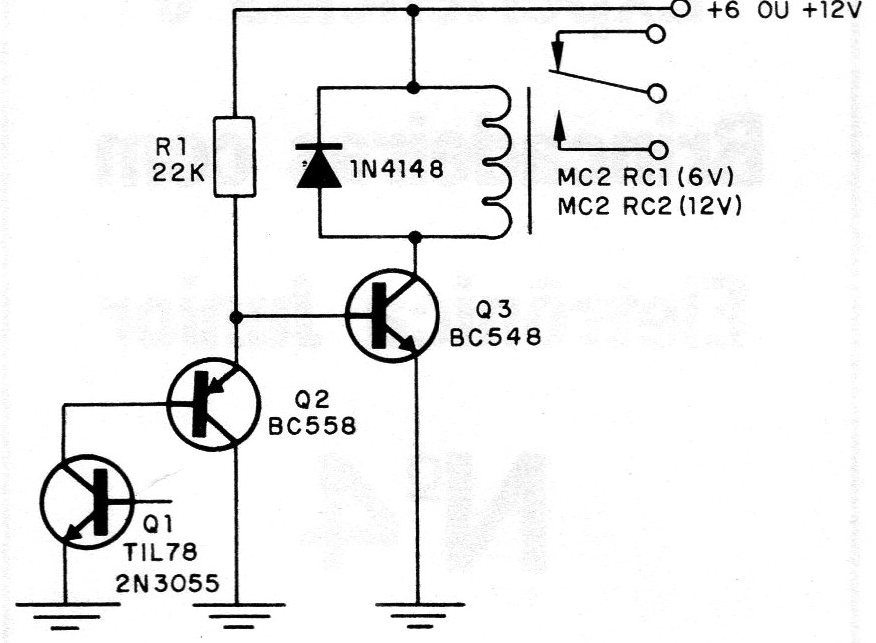
In the figure we have a circuit in which complementary transistors are used to obtain greater sensitivity in the activation by the interruption of the light. The illuminated phototransistor causes the BC558 (PNP) transistor to polarize in the sense of conducting it. The low resistance presented between the emitter and the collector of this transistor polarizes the NPN transistor to take it to cut. In these conditions, the current that circulates between the emitter and the collector of the BC548 transistor is insufficient to activate the relay. With the illumination cut, the BC558 transistor stops driving, which allows the 22k resistor to polarize the BC548 transistor in the sense of having its full conduction (saturation). The relay is then driven by a current that drives it. The sensitivity adjustment in this circuit can be added by connecting, in series with the 22k resistor, a 47k potentiometer.