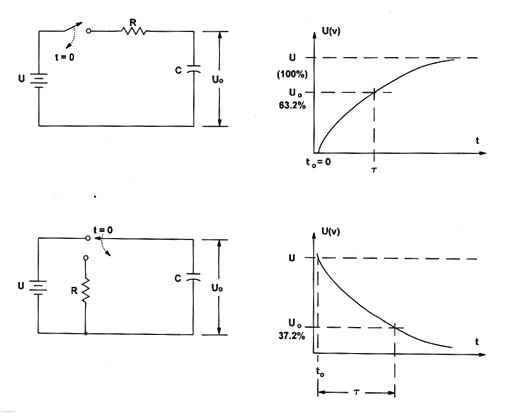
The time constant of an RC circuit is the time interval needed to either charge the capacitor via a resistor to 63,2% of the total charge, or discharge from the total charge to 37,8%.
Formula 1
T = R x C
Where
T is the time constant in seconds (s)
R is the resistance in ohm (Ω)
C is the capacitance in farads (F)
If multiples or submultiples are used the next cases can be considered:
Microfarads – the time Will be found in microseconds
Nanofards – the time Will be found in nanoseconds
Picofarads – the time Will be found in picoseconds
(see table)
Derivated Formulas:
Formula 2
R = T / C
Formula 3
C = T / R
Table – Time Calculations
| When using R in | and C in | T Will be found |
| ohms | farads | segundos |
| ohms | microfarads | microssegundos |
| quilohms | farads | quilossegundos |
| quilohms | microfarads | milissegundos |
| megohms | microfarads | segundos |
Application example:
Determine the time Constant of a circuit formed by a 100 kohm resistor in series with a 500 microfarad capacitor. Calculate the voltage across the circuit after the considered time interval when the circuit is subjected to a 100V power supply.
Data:
R = 100 x 103 Ω
C = 500 x 10-6 farads
T = ?
Using Formula 1:
T = 100 x 103 x 500 x 10-6 = 50 seconds
Final voltage:
V = 0,63 x 100 = 63,2 V



