A microampere dc current through your fingers can control heavy-duty loads such as home appliances, motors, and heaters up to 8,800 W.
The circuit consists of a bistable touch-controlled multivibrator that drives a TRIAC through a unijunction transistor (UJ T) and an isolating transformer. The TRIAC, a TIC226-B, is rated for loads up to 800 W (8 A, 117 V) and must be mounted on a heatsink.
Wires to the touch plates can be as long as you want, and you can place it some distance from the circuit to be controlled. As the control line operates with a low voltage and low current, no special care needs to be taken with the connection.
A schematic diagram of the Full-Wave Touch Switch for AC Loads is given in Fig. 1.
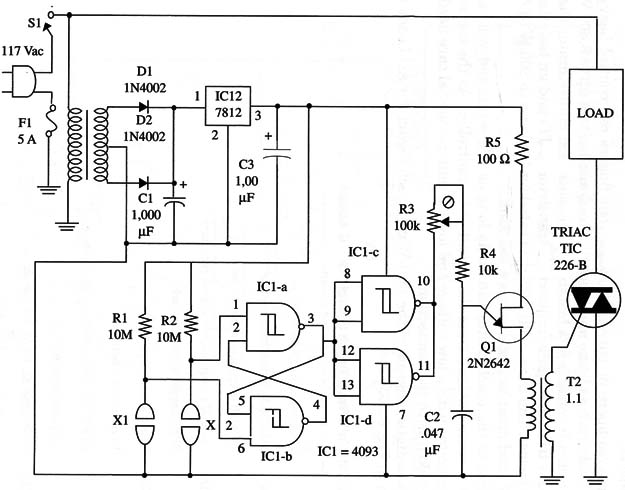
Make sure that the ac high current line isn't connected to the board and that the wire used is appropriate for this task. The TRIAC must be mounted on a large heatsink.
T2 is a pulse transformer (1:1) as used in many circuits to trigger SCRs and TRIACs. X1 and X2 are touch switches made with two small metal plates that are simultaneously touched by the fingers. R3 is adjusted to the maximum power of the load when the circuit is on.
IC1 4093 CMOS integrated circuit
IC2 7812 voltage regulator IC
TRIAC TIC226-B, Texas Instruments
Q1 2N2646 unijunction transistor
D1, D2 1N4002 or equivalent silicon rectifiers
S1 SPST toggle or slide switch
X1, X2 Touch sensor (see text)
F1 10 A fuse and holder
T1 12.6 V, GT, 300 to 500 mA transformer
T2 1:1 pulse transformer
R1, R2 10,000,000 ohm, 1/4 W, 5% resistors
R3 100,000 ohm trimmer potentiometer
R4 10,000 ohm, 1/4 W, 5% resistor
C1 1,000 µF, 25 WVDC electrolytic capacitor
C2 0.047 µF ceramic or metal film capacitor
C3 100 µF, 16 WVDC electrolytic capacitor



