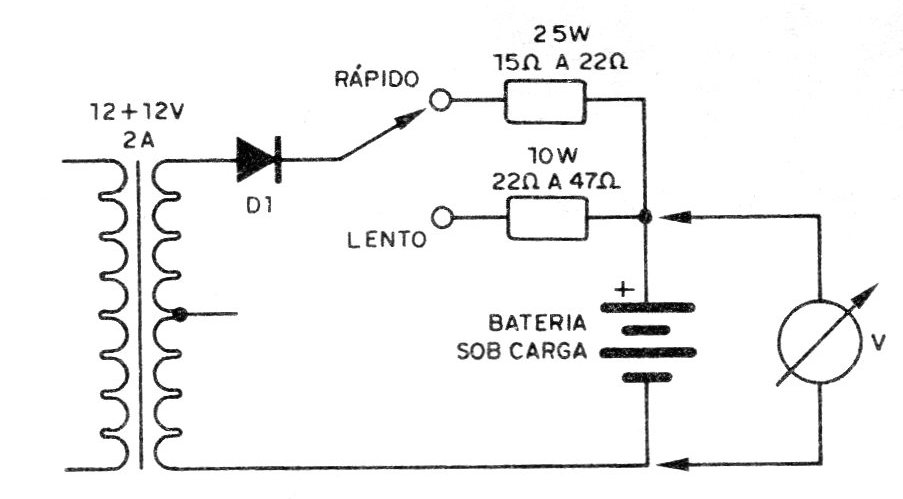
Car battery charging can be done very simply with the indicated circuit. Although in the "fast" position, using a small transformer, we have a current of only 2 A, which does not give the same speed as the "professional" chargers, this current is enough to leave a battery in " conditions to start a vehicle. In the slow position, the charge is already made with a lower current, which is recommended to obtain longer battery life. The transformer used is 12 + 12 V with 2 A of current and the diode is for 2 A with at least 50 V of peak inverse voltage (PIV). It is the two resistors that determine the value of the maximum load current, and must be of high dissipation, of wire, with at least 25 W the smallest and at least 10 W the largest (in value). The charged battery can be either 6 or 12 V for vehicles, and a voltmeter indicates when the rated voltage is reached. This can be the type of movable iron for greater savings. We remind you that this circuit is not automatic, and that any sign of heating of the components can indicate that the battery is shorted, not allowing more load (The resistors work hot, but the other components do not.)