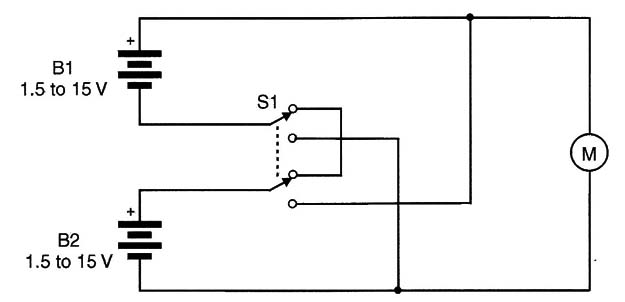
The motors used in this application must have the same characteristics (voltage and current).
When they are wired in parallel, each is powered by the main power supply voltage. When they are wired in series, the voltage is divided by two, and each one receives half of the supply voltage while running in a low-speed mode.
But the circuit does not always behave in this manner. If one motor is loaded more easily than the other, the voltage will no longer be divided by two. The heavily loaded motor will be powered by a lower voltage, and the other will run with higher Jltage. In other words, in this circuit, the voltage across each motor depends on the load.



