The integrated circuit LM350 consists of a linear voltage regulator, which can also be configured as a current regulator, capable of supplying loads up to 3 A. In figure 1 we have the pinning of this component. Note that, unlike many common voltage regulators, the center pin is not the (Adj) setting, but the output. This is justified because in power components, the central pin is also attached to the tab (tab) to aid in heat dissipation of the component, which must be mounted on a heat radiator. The T-suffix of this component indicates the TO-220 envelope, since there is the same with another TO-5 metallic envelope component.
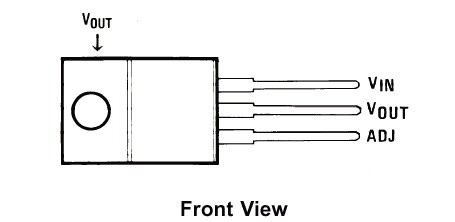
The LM350 integrated circuit also has important features for the project of sources such as protection against short circuits, short protection or shutdown when overheating, and provides excellent regulation reflected in the source described. We also note that the LM350-T has an 1.2 Vinternal zener diode for reference, hence this is the minimum voltage of the circuit, because when Adj is grounded, at least the setting, the diode in question remains in the circuit setting this value The minimum output voltage.
Assembly
In figure 2 we have the complete diagram of the power supply.
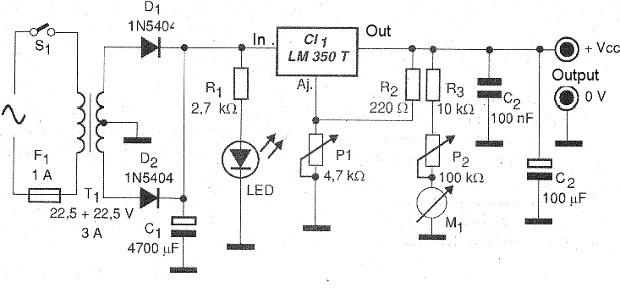
Its assembly can be made based on a terminal strip (since the circuit is not critical) or on a printed circuit board, with the pattern shown in figure 3.
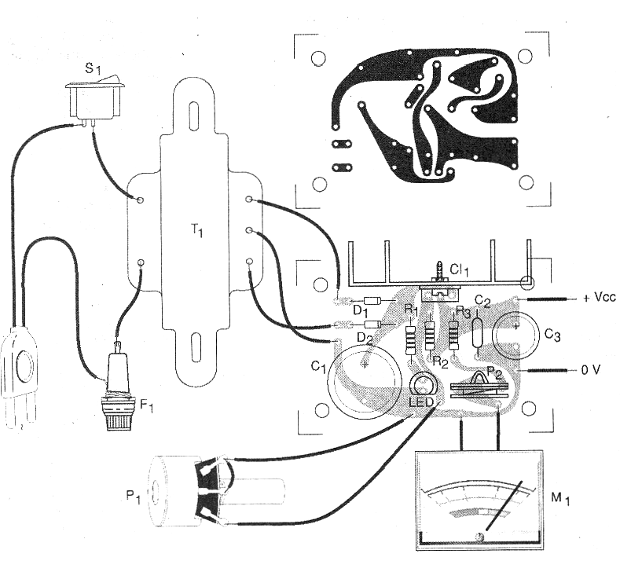
We note that in the case of the printed circuit board, the tracks through which the strongest currents pass must be kept wide. It is customary to leave at least 1mm wide for each amp, which implies 3mm tracks for the main currents provided by this source.
The transformer is the component that will basically determine the maximum output voltage. The maximum output voltage will be approximately 2 V below the input voltage of the circuit. This voltage will also depend on the value of P1 which can be from 2.2 k ohm to 4.7 k ohm. It is also important that the transformer is of good quality, actually being able to supply a current of 3 A, mainly with the higher output voltages.
A poor quality transformer may experience a voltage drop when more intense currents are requested, thus affecting the higher output voltages. The integrated circuit should be mounted on a good heat radiator, and if possible even out of the box. The positions of all polarized components, diodes, electrolytic capacitors and others, must be observed.
To indicate the output voltage, there are several options, such as an analogue indicator consisting of a 0-200 uA microammeter with a 10 k ohm resistor in series with a 100 k ohm trimpot. A 0-1 mA milliammeter can also be used for the same purpose and the calibration will be obtained based on the indications of a common multimeter.
Another possibility is to use a 3 ½ digit digital module as the ones that can be obtained based On the integrated circuit 7106 (Intersil). These modules can be easily configured as digital voltmeters with good accuracy. Finally, an interesting (and even economical) solution is to embed a low-cost multimeter, which can even be found in supermarkets, by setting its scale to DC volts and using its output indications, as shown Figure 4.
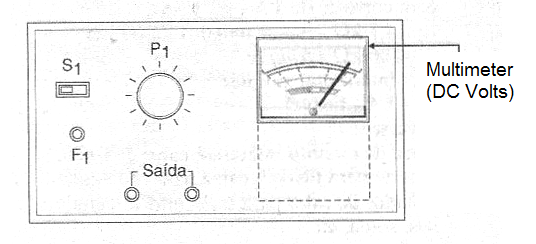
The voltage output can be made from terminals (red and black), to the type that also has fits for banana plugs.
Thus, the reader can also count on a pair of cables (red and black) with alligator clips, facilitating its connection in the source and feeding of external circuits, as shown in figure 5.
Test ing and Use
Once the assembly is complete, check it carefully and if everything is in order, connect your power supply to the mains. For initial testing connect a multimeter to the output and as load a 15 ohm resistor to 50 ohms x 10 W at the output.
Turning on the power supply, the voltage indicated by the multimeter must increase to the maximum value set. If it stops earlier than expected, it may be a signal that the transformer does not actually provide the maximum current expected.
To use, always observe the maximum current that the power supply can supply and observe the polarity of the connected circuit connection as an accidental inversion can cause it to burn. Never change the supply voltage of a sensitive load, such as an electronic device, when it is connected to the power source. Always turn off the load first, change the voltage, and then turn it on again.
CI-1 - LM350T - integrated circuit, voltage regulator
D1, D2 - 1N5404 - silicon rectifier diodes
D3 - 1N4002 - silicon rectifier diode
LED1 - Common red LED
C1 - 4 700 uF or 10 000 uF x 40 V - electrolytic capacitor
C2 - 100 nF - ceramic capacitor
C3 - 100 uF x 36 V - electrolytic capacitor
R1 - 2.7 k ohm x 1/8 W - resistor - red, violet, red
R2 - 220 ohm x ½ W - resistor - red, red, brown
R3 - 10 k ohm x 1/8 W - resistor - brown, black, orange
M1 - 100 uA - moving coil indicator
T1 - Transformer with primary according to the local voltage grid and secondary from 22.5 to 25 V with current of 3 A - see text
P1 - 4.7 k ohm - lin or log potentiometer
P2 -100 k ohm - trimpot
S1 – On/Off switch
F1 - 1 A - fuse
Miscellaneous:
Printed circuit board, power cable, fuse holder, mounting box, heat radiator for the integrated circuit, wires, solder, etc.



